Abstract
The Prague texture segmentation data-generator and benchmark is a web based (http://mosaic.utia.cas.cz) service designed to mutually compare and rank different static or dynamic texture segmenters, and to support new supervised or unsupervised classification methods development. The benchmark verifies their performance characteristics on monospectral, multispectral, bidirectional texture function (BTF), satellite or dynamic texture data and enables to test their noise robustness, scale, and rotation or illumination invariance.Prague Texture Segmentation Datagenerator and Benchmark
The purpose of PTSDB web service [link] is
- to mutually compare and rank different (dynamic/static) texture segmenters (supervised or unsupervised),
- to support new segmentation and classification methods development.
The service allows (U = for registered users only)
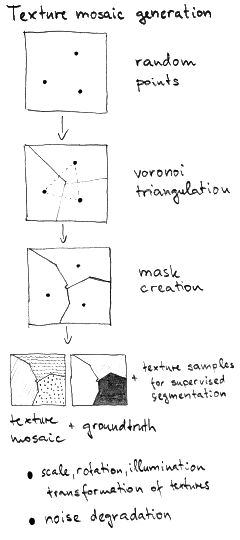
- to obtain customized experimental texture mosaics and their corresponding ground truth (U),
- to obtain the benchmark texture mosaic set with their corresponding ground truth,
- to evaluate your working segmentation results and compare them with the state of art algorithms (U),
- to include your algorithm (reference, abstract, benchmark results) into the benchmark database (U),
- to check single mosaics evaluation details (criteria values and resulted thematic maps),
- to rank segmentation algorithms according to the most common benchmark criteria,
- to obtain LaTeX coded resulting criteria tables or export data in MATLAB format (U),
- to select user-defined subset of criteria (U).
Dataset
- Computer generated texture mosaics and benchmarks are composed from the following image types:
- monospectral textures,
- multispectral textures,
- BTF (bidirectional texture function) textures [BTF Bonn Database],
- ALI hyperspectral satellite images [Earth Observing 1],
- dynamic textures [DynTex],
- rotation invariant texture set,
- scale invariant texture set,
- illumination invariant texture set.
- All generated texture mosaics can be corrupted with additive Gaussian noise, Poisson or salt&pepper noise.
- The corresponding trainee sets (hold out) are supplied in the classification (supervised) mode.
Benchmark evaluation
- Submitted results are stored in the server database and used for the algorithm ranking based on a selected criterion from the following criteria set:
- average RANK (over displayed criteria),
- region-based (including the sensitivity graphs):
- CS - correct segmentation,
- OS - over-segmentation,
- US - under-segmentation,
- ME - missed error,
- NE - noise error,
- pixel-wise:
- O - omission error,
- C - commission error,
- CA - class accuracy,
- CO - recall = correct assignment,
- CC - precision = object accuracy,
- I. - type I error,
- II. - type II error,
- EA - mean class accuracy estimate,
- MS - mapping score,
- RM - root mean square proportion estimation error,
- CI - comparison index,
- F-measure (weighted harmonic mean of precision and recall) graph,
- consistency measures:
- GCE - global consistency error,
- LCE - local consistency error,
- clustering:
- dM - Mirkin metric,
- dD - Van Dongen metric,
- dVI - variation of information.
- Result values for dynamic benchmark are averages of criteria values over all video frames.

Authors
- Stanislav Mikes
- Michael Haindl
Please quote and consult for further information:
Haindl, M. - Mikeš, S.: Texture Segmentation Benchmark. Proc. 19th International Conference on Pattern Recognition. IEEE Computer Society, 2008. ISBN 978-1-4244-2174-9, ISSN 1051-4651, pp. 1-4
Haindl, M. - Mikeš, S.: Texture Segmentation Benchmark. Proc. 19th International Conference on Pattern Recognition. IEEE Computer Society, 2008. ISBN 978-1-4244-2174-9, ISSN 1051-4651, pp. 1-4



